Government Surveillance: Are You Being Watched?
The Historical Context of Government Surveillance
Government surveillance has roots that can be traced back centuries. From the use of spies in ancient empires to the early days of telegraph communications, authorities have always sought information to maintain power and enhance security. The 20th century marked a significant evolution in surveillance capabilities, particularly with the advent of technology during World War II and the subsequent Cold War era. Nations adopted advanced methods, such as wiretapping and signal intelligence, to monitor potential threats.
Legislative Frameworks and Regulations
In modern societies, government surveillance operates within a framework of laws that attempt to balance national security interests with individual privacy rights. In the United States, the Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Act (FISA), enacted in 1978, governs the collection of foreign intelligence information through electronic surveillance. The Patriot Act, passed after the September 11 attacks, expanded law enforcement’s surveillance authority, allowing for more extensive monitoring of communications. Critics argue that such laws often infringe on civil liberties, blurring the line between safety and privacy.
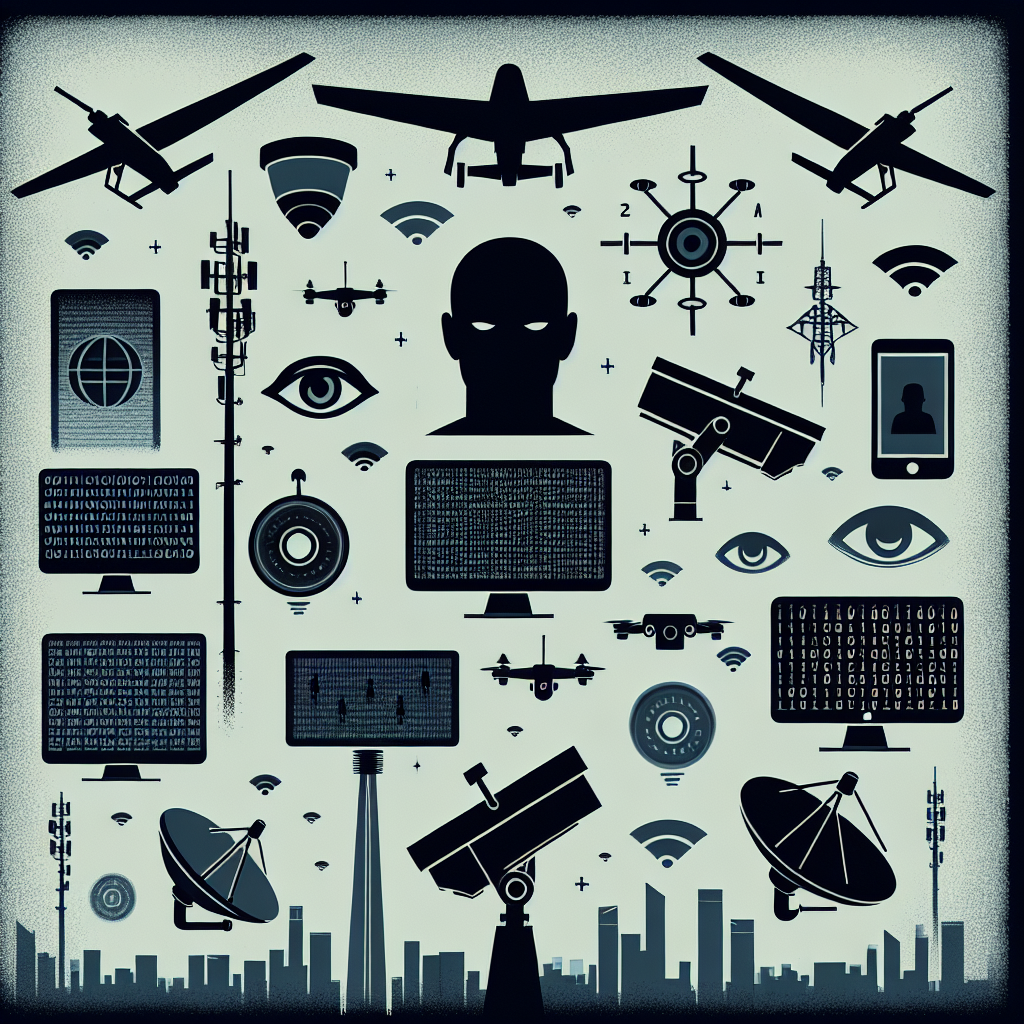
Types of Surveillance Techniques
-
Electronic Surveillance: This includes monitoring communications via phone tapping, email interception, or data collection from social media platforms. Governments often justify these actions for counterterrorism or crime prevention.
-
CCTV Monitoring: Closed-circuit television cameras have become ubiquitous in urban areas worldwide. Many cities have installed extensive networks of surveillance cameras, claiming they provide security benefits. However, studies raise concerns about their effectiveness versus the invasion of public space privacy.
-
Data Collection: Governments often gather vast amounts of data through various means, including internet service providers and mobile phone companies. This data can include anything from location tracking to usage patterns, creating detailed profiles of individuals.
-
Facial Recognition Technology: This biometric software can identify individuals from images and video. While touted as a tool for enhancing public safety, concerns over accuracy, discrimination, and consent are significant.
The Role of Technology in Surveillance
Technological advancements have significantly impacted the scope and efficiency of government surveillance. The rise of the digital age opened new avenues for data collection. Algorithms can analyze vast datasets to uncover suspicious activities, while artificial intelligence enhances predictive capabilities. However, the more advanced the technology, the greater the risk of misuse, leading to questions about ethical standards and oversight.
Surveillance and Civil Liberties
The balance between surveillance and civil liberties is hotly debated. Proponents of expanded surveillance argue that enhanced monitoring helps prevent criminal activities and terrorist attacks. Conversely, civil libertarians assert that such measures stifle free speech, promote fear, and violate constitutional rights. Cases like the NSA’s mass data collection revealed by Edward Snowden brought national and international attention to concerns regarding privacy violations.
The Global Landscape of Surveillance
Government surveillance practices vary globally. In China, for instance, surveillance is pervasive, involving a vast network of cameras and monitoring systems supported by artificial intelligence. The government’s use of technology to track citizens, particularly marginalized groups, raises international human rights alarms.
In contrast, countries like Germany have stringent privacy laws stemming from historical abuses of state surveillance during the Nazi regime and the Stasi era in East Germany. Such historical context shapes the public’s perception and acceptance of government monitoring measures.
Public Awareness and Attitudes
Public knowledge about surveillance varies significantly. Many individuals remain unaware of the extent and implications of surveillance programs. Polls indicate that while some people express concern over surveillance, they often prioritize security over privacy. This paradox can foster complacency, culminating in limited public discourse about citizenship rights and government overreach.
The Debate Around Transparency and Accountability
For government surveillance to be viewed as legitimate, advocates emphasize the need for transparency and accountability. Calls for independent oversight bodies capable of reviewing surveillance practices are essential to ensure that surveillance does not escalate into a tool of oppression. Additionally, legislative reforms are suggested to ensure that citizens are informed about how their data is used and the reasons behind surveillance operations.
The Impact of Big Tech on Surveillance
The role of Big Tech companies in government surveillance cannot be understated. These entities collect vast quantities of user data and often collaborate with state actors. While companies insist on protecting user privacy, data breaches and scandals – such as the Facebook-Cambridge Analytica incident – have raised alarms about vulnerabilities and ethical implications surrounding user consent and data handling.
The Future of Surveillance
As technological innovations, such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and 5G networks, continue to advance, the potential for increased surveillance complexity grows. Smart devices in homes can collect vast amounts of data, making it feasible for governments to monitor citizens in unprecedented ways. The amplification of surveillance capabilities raises severe ethical questions concerning informed consent and privacy rights in a digitized world.
Conclusion
Government surveillance permeates everyday life, raising essential questions about the balance between security and privacy. As technology advances, individuals must remain vigilant and informed regarding their rights and the mechanisms that govern surveillance. Engaging in meaningful conversations about surveillance can empower citizens to shape policies that respect individual freedoms while ensuring national safety.
FAQs on Government Surveillance
1. How do I know if I am being surveilled?
While it is challenging to detect government surveillance, signs might include strange phone behaviors or rapid battery drainage on devices.
2. Is government surveillance legal?
Yes, under specific conditions governed by laws, but it often raises concerns regarding civil liberties and privacy.
3. How can I protect my privacy online?
Utilizing VPNs, encryption tools, and practicing digital hygiene can enhance online privacy.
4. What should I do if I believe my rights have been violated?
Consult legal experts or organizations specializing in civil rights for guidance and support.
By remaining informed and discussing surveillance matters openly, citizens can play an active role in shaping a balanced approach to security and privacy.












Leave a Reply